By 2025, Gartner predicts that a staggering 80% of enterprises will have shut down their traditional data centers. This mass exodus to the cloud signals a paradigm shift in how businesses manage their IT resources, driven by the promise of greater agility, scalability, and cost-efficiency. Yet, a successful cloud migration is not merely about moving data from on-premises servers to virtual environments; it’s about embracing a fundamental transformation in how businesses operate and innovate.
The allure of the cloud is undeniable. It offers the potential to reduce capital expenditures, streamline IT operations, and access cutting-edge technologies that were once out of reach for many organizations. However, the path to cloud adoption is not without its challenges. It requires careful planning, meticulous execution, and a deep understanding of the organization’s unique needs and goals.
Migrating to the cloud is not a one-size-fits-all endeavor. Different businesses have diverse IT landscapes, varying levels of cloud readiness, and unique regulatory constraints. A successful migration requires a tailored approach that takes into account these factors and aligns with the organization’s overall business strategy.
This comprehensive guide will serve as your trusted companion on your cloud migration journey. We will delve into the fundamental concepts of cloud computing, explore the different types of cloud migration strategies, and provide a step-by-step roadmap for a successful transition. We will also address the common challenges that organizations face during migration and offer best practices for mitigating risks and ensuring a smooth and seamless transition.
Furthermore, we will showcase real-world examples of companies that have successfully migrated to the cloud and reaped significant benefits in terms of cost savings, operational efficiency, and innovation. These case studies will provide valuable insights and inspiration for businesses considering or embarking on their own cloud migration initiatives.
By the end of this exploration, you will be equipped with the knowledge and tools necessary to navigate the cloud landscape with confidence. Whether you are a small business owner looking to streamline your IT operations or a large enterprise seeking to unlock the full potential of cloud computing, this guide will provide you with a comprehensive framework for a successful cloud migration.
Understanding Cloud Migration: A Paradigm Shift in IT
Cloud migration, at its core, is the process of relocating your digital assets and operations from traditional on-premises infrastructure to a virtualized environment hosted by a cloud service provider. This shift allows businesses to leverage the cloud’s virtually limitless resources, eliminating the need for extensive hardware investments and maintenance.
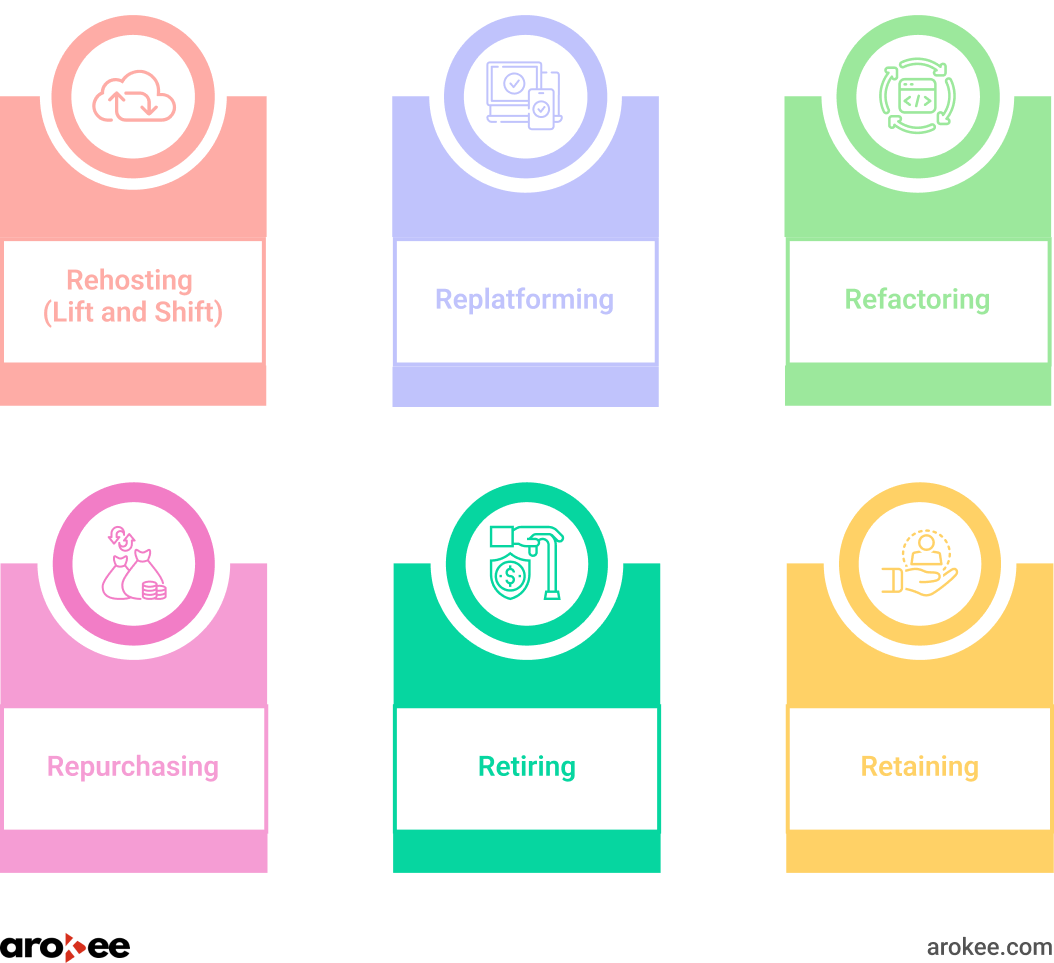
There are several distinct approaches to cloud migration, each tailored to the specific needs and objectives of an organization:
- Rehosting (Lift and Shift): This approach involves migrating applications to the cloud as-is, with minimal changes. It’s a quick and relatively straightforward way to get started with cloud adoption and realize immediate benefits like cost savings and improved scalability.
- Replatforming: In this approach, some optimizations are made to applications during the migration process to leverage cloud-native features, without significantly altering their core architecture. This can lead to improved performance and cost efficiency.
- Refactoring: Refactoring entails a more comprehensive redesign of applications to take full advantage of cloud-native technologies. This approach unlocks the cloud’s full potential for scalability, agility, and innovation, but it also requires more time and resources.
- Repurchasing: This involves replacing legacy applications with cloud-based Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) solutions. SaaS offerings can provide significant advantages in terms of cost savings, scalability, and ease of maintenance.
- Retiring: Outdated or redundant applications are decommissioned during the migration process, streamlining the IT landscape and reducing complexity.
- Retaining: Some applications might need to remain on-premises due to regulatory requirements, technical constraints, or other business-specific reasons.
The cloud migration process typically involves several key phases:
- Assessment: A thorough evaluation of the existing IT environment is conducted to understand the current infrastructure, applications, data, and dependencies. This assessment helps in determining the most suitable migration strategy and identifying potential challenges.
- Planning: A detailed migration plan is developed, outlining the migration timeline, resource allocation, budget, and risk mitigation strategies. This plan serves as a roadmap for the entire migration process.
- Execution: The actual transfer of data and applications to the cloud takes place, often in a phased manner to minimize disruption and allow for adjustments as needed.
- Testing: Rigorous testing is conducted to ensure that all systems and applications function correctly in the new cloud environment. This includes functional testing, performance testing, and security testing.
- Optimization: After the migration, continuous monitoring and optimization are essential to ensure optimal performance, cost efficiency, and security. This involves fine-tuning configurations, adjusting resource allocation, and implementing best practices for cloud management.
Benefits of Cloud Migration
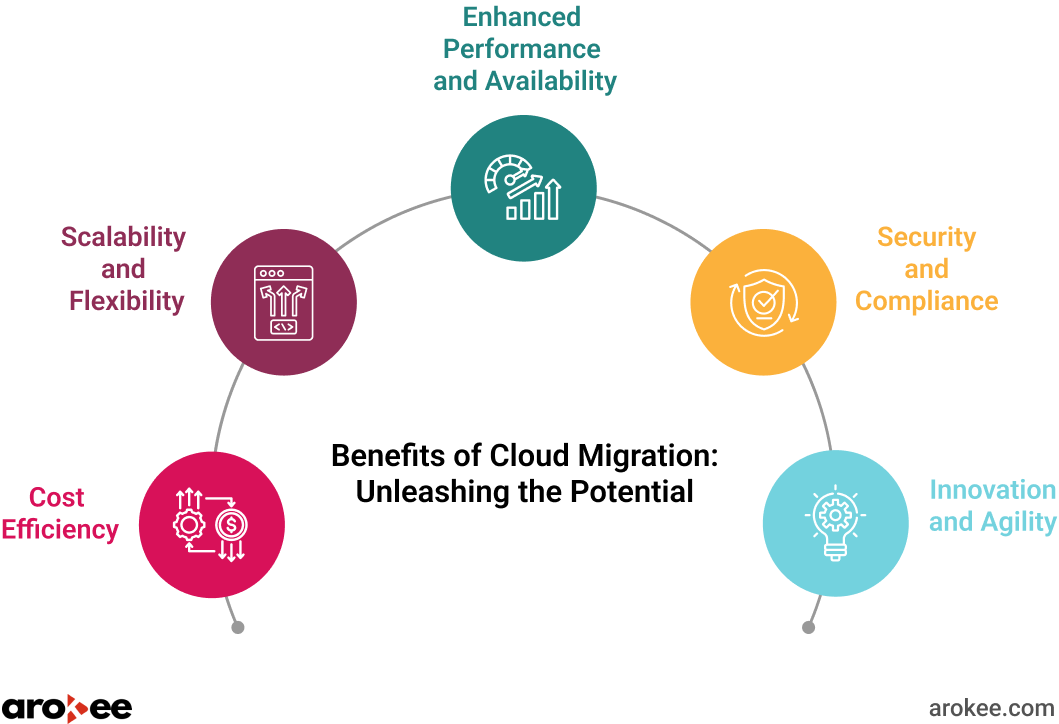
Migrating to the cloud offers a multitude of advantages that can revolutionize the way businesses operate and compete:
- Cost Efficiency: One of the most compelling reasons for cloud migration is the significant cost reduction it offers. By eliminating the need for large upfront investments in hardware and software, businesses can shift from capital expenditures (CapEx) to operational expenditures (OpEx). The pay-as-you-go model of cloud computing ensures that organizations only pay for the resources they actually consume, leading to predictable and manageable IT costs.
- Scalability and Flexibility: The cloud’s inherent elasticity allows businesses to scale their IT resources up or down effortlessly, based on demand. This scalability is particularly valuable for businesses with fluctuating workloads, seasonal spikes, or ambitious growth plans. With the cloud, you can quickly provision additional resources during peak periods and scale back when demand subsides, ensuring optimal performance and cost efficiency.
- Enhanced Performance and Availability: Cloud providers operate cutting-edge data centers with high-performance computing infrastructure, redundant networks, and robust disaster recovery mechanisms. This translates to faster application response times, reduced downtime, and improved overall reliability for your business-critical applications and services.
- Security and Compliance: Leading cloud providers invest heavily in security measures, employing advanced technologies like encryption, access controls, and threat detection to protect your data. They also adhere to strict compliance standards, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and SOC 2, ensuring that your data is handled in accordance with industry regulations.
Innovation and Agility: The cloud fosters innovation by providing access to a vast array of cutting-edge technologies and services, including AI, machine learning, big data analytics, and the Internet of Things (IoT). Cloud-based development environments enable rapid prototyping and deployment of new applications, empowering businesses to stay ahead of the curve.
Challenges of Cloud Migration: Navigating the Complexities
While the benefits of cloud migration are enticing, it’s essential to be aware of the challenges that may arise during the journey:
- Complexity of Migration: Migrating complex applications and legacy systems to the cloud can be a daunting task. It requires careful planning, thorough testing, and meticulous execution to ensure a seamless transition and avoid disruptions to business operations.
- Data Security and Privacy Concerns: The security of sensitive data is a top concern for any organization considering cloud migration. Ensuring data protection during transit and at rest, as well as maintaining compliance with data privacy regulations, necessitates robust security measures and careful consideration of data governance policies.
- Downtime and Business Continuity: Minimizing downtime during the migration process is critical to maintaining business operations and customer satisfaction. A well-thought-out migration plan with contingencies for unexpected disruptions is essential to ensure continuity.
- Cost Management: While cloud computing offers cost savings in the long run, it’s crucial to manage migration costs effectively. This includes accounting for data transfer fees, potential overprovisioning of resources, and ongoing cloud service charges.
- Skill Gaps and Training: Cloud migration often requires specialized skills that may not be readily available within an organization. Investing in training programs or partnering with cloud experts can help bridge the knowledge gap and ensure a smooth transition.
Best Practices for Cloud Migration: A Roadmap to Success
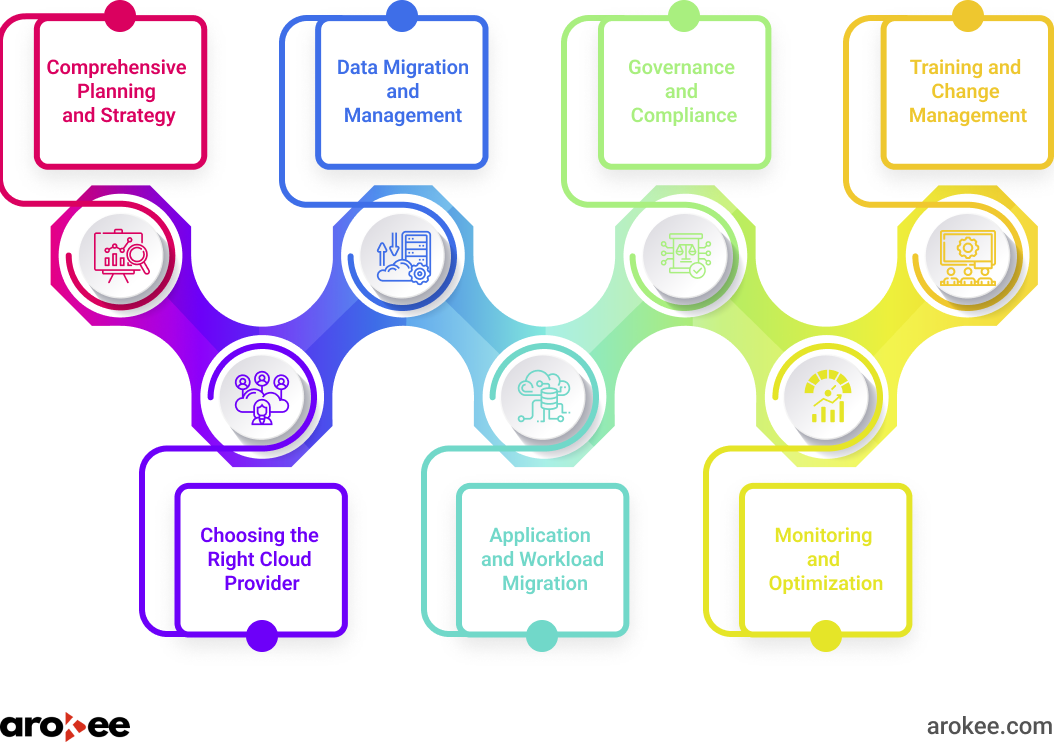
To navigate the complexities of cloud migration and maximize its benefits, organizations should adhere to a set of best practices:
- Comprehensive Planning and Strategy: Develop a detailed migration plan that outlines clear objectives, timelines, resource allocation, and risk mitigation strategies. This plan should encompass all aspects of the migration, from data and application migration to security and compliance.
- Choosing the Right Cloud Provider: Carefully evaluate different cloud providers based on their service offerings, pricing models, security measures, and compliance certifications. Select a provider that aligns with your specific needs and offers robust support services.
- Data Migration and Management: Implement robust data migration strategies, ensuring data integrity and security throughout the process. Consider different approaches like big bang, phased, or hybrid migration based on your specific requirements and risk tolerance.
- Application and Workload Migration: Prioritize applications for migration based on their business criticality and potential for cloud optimization. Refactor or re-architect applications to leverage cloud-native features for improved performance and scalability.
- Governance and Compliance: Establish comprehensive governance policies that define roles, responsibilities, and processes for cloud usage. Ensure ongoing compliance with relevant regulations and industry standards to protect data and mitigate risks.
- Monitoring and Optimization: Implement robust monitoring tools to track performance, resource utilization, and security threats in the cloud environment. Continuously optimize your cloud infrastructure to achieve maximum efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
- Training and Change Management: Invest in training programs to equip your workforce with the necessary skills to manage and leverage cloud technologies effectively. Communicate the benefits of cloud migration to stakeholders and address any concerns they may have to foster a smooth transition.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
Real-world examples illustrate the transformative power of cloud migration:
- Netflix: The streaming giant’s migration to the cloud enabled it to scale rapidly and deliver seamless streaming experiences to millions of users worldwide. By leveraging the cloud’s scalability, Netflix was able to expand its services rapidly, ensuring smooth playback even during peak usage periods.
- Airbnb: The online marketplace for lodging and homestays faced the challenge of scaling its platform to accommodate millions of listings and bookings across the globe. By migrating to the cloud, Airbnb achieved the flexibility and scalability it needed to handle exponential growth while maintaining high performance and availability.
- Capital One: This financial services giant embraced cloud computing to enhance its agility and accelerate innovation. The move to the cloud allowed Capital One to rapidly deploy new features and services, improve customer experiences, and streamline its IT operations.
- GE Oil & Gas: In a complex industrial setting, GE Oil & Gas migrated its mission-critical applications to the cloud to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance collaboration across its global operations. The cloud-based platform enabled real-time data analysis and remote monitoring of equipment, leading to improved decision-making and predictive maintenance.
- Coca-Cola: The beverage giant migrated its SAP environment to the cloud, resulting in significant cost savings and improved operational efficiency. The move to the cloud also enhanced Coca-Cola’s ability to analyze data and gain insights into consumer behavior, driving more effective marketing and sales strategies.
- Spotify: The popular music streaming service relies heavily on the cloud to deliver a seamless user experience to millions of subscribers worldwide. By leveraging the cloud’s scalability and high availability, Spotify ensures uninterrupted music streaming, personalized recommendations, and efficient data management.
These real-world examples underscore the diverse applications and transformative potential of cloud migration across industries. From enabling global expansion to improving operational efficiency, enhancing customer experiences, and fostering innovation, the cloud has become a catalyst for businesses to achieve their strategic goals and gain a competitive edge.
Future Trends in Cloud Migration: Charting the Course Ahead
The cloud computing landscape is a dynamic and ever-evolving realm, with several trends shaping its future trajectory:
- Edge Computing: Edge computing is gaining momentum as a complementary technology to cloud computing. By bringing computation and data storage closer to the source, edge computing reduces latency, improves real-time processing capabilities, and enables applications like IoT and autonomous vehicles to operate more efficiently.
- Serverless Computing: This emerging paradigm abstracts away the complexities of server management, allowing developers to focus solely on writing code. Serverless computing offers unprecedented scalability and cost-efficiency, making it an attractive option for businesses seeking to streamline their IT operations.
- AI and Machine Learning in Cloud Migration: Artificial intelligence and machine learning are playing an increasingly vital role in cloud migration. These technologies automate complex tasks, optimize resource allocation, and enhance security, making the migration process smoother and more efficient.
- Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud Environments: To avoid vendor lock-in and leverage the unique strengths of different cloud providers, many organizations are adopting multi-cloud and hybrid cloud strategies. This approach offers greater flexibility, resilience, and the ability to optimize workloads across multiple cloud platforms.
- Sustainability in the Cloud: As environmental concerns grow, cloud providers are increasingly focusing on sustainability initiatives. This includes using renewable energy sources to power data centers, implementing energy-efficient hardware, and developing tools to help customers track and reduce their carbon footprint.
Conclusion: Embark on Your Cloud Journey with Confidence
Cloud migration is no longer a luxury but a strategic imperative for businesses seeking to thrive in the digital age. The cloud’s ability to provide scalability, flexibility, cost-efficiency, and access to cutting-edge technologies makes it an indispensable tool for driving growth and innovation.
While the migration process can be complex, the benefits far outweigh the challenges. By following best practices, carefully selecting the right cloud provider, and continuously optimizing your cloud environment, you can unlock the full potential of cloud computing and position your business for long-term success.
As you embark on your cloud journey, remember that it’s not just about moving your data and applications; it’s about transforming your entire IT ecosystem. The cloud offers a wealth of opportunities for businesses to streamline operations, enhance customer experiences, and drive innovation. By embracing the cloud, you can embark on a transformative journey that will propel your organization into the future of digital business.

